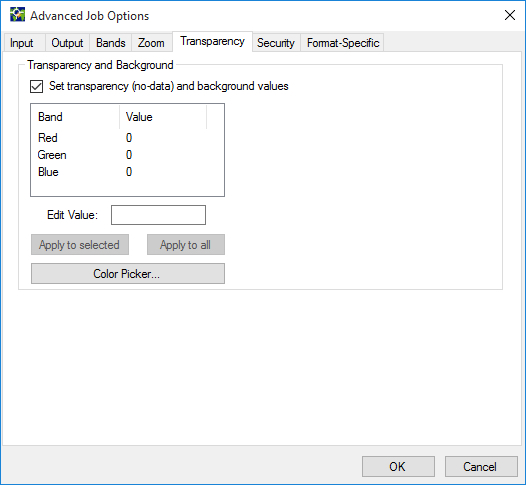
When you select MG2, MG3, or JPEG 2000 as the image output format, you can use the options on the Transparency tab to define the color of transparency and background areas. One color must serve for both the transparency and background values.
You can specify colors based on the color space (RGB/grayscale) and color depth (8-bit/16-bit) of the source image.

The transparency and background color setting must be within the range of pixel values that the image's data type supports (e.g. 0 – 255 for 8-bit images and 0 – 65,535 for 16-bit images). These values are derived from the native metadata for an input image.
To select an alternate transparency and background color do one of the following:
The effects of the transparency options can be simulated in the Preview tab.
NOTE: The MG4 format stores transparency in an alpha band whereas MG3, MG2, and JPEG 2000 images map transparency to a specific color. If your input image is in the MG4 format, and if the output format is MG3, MG2, or JPEG 2000, transparency is mapped to the transparency color that you specify.
You can select an 8-bit RGB color value from the color palette or Color Picker if the source image is an 8-bit RGB.
GeoExpress uses the standard Windows color picker interface, which allows you to add custom colors. See your Microsoft Windows or Microsoft Office documentation for more information about picking colors.
All images in the MrSID format are in either grayscale or RGB mode. Color images are RGB; black-and-white images are grayscale. Any black-and-white image encoded by GeoExpress, if not already in grayscale mode, is converted to grayscale; any color image, if not already RGB (for instance, an indexed color image), is converted to RGB.
To specify a transparency pixel value, determine the RGB value of the transparency area in the source image. Most commonly, this will be black (0-0-0) or white (255-255-255). If desired, use a color-finder program to read the transparency RGB values. Once the RGB values for the transparency area have been determined, they must be entered manually.
The RGB color scale for an 8-bit image, with values of 0-255 for the colors red, green, and blue, is capable of accurately displaying 16,777,216 colors. An indexed color image selects colors from a scale containing 256 colors. Each color in an indexed color image is specified using a value from 0 to 255.
Due to the wide variety of indexed-color valuing systems available, a specific color in one indexed color image can be given one value, while the same color in another image is given a different value. For example, a color with a single RGB value may be given an indexed color value of 120 by one imaging application and 142 by another.
For this reason, any time the input or output transparency options are used with indexed color images, the indexed color values must be read in as RGB and entered manually.
If desired, use a color-finder program to read the transparency RGB values.